CLINICAL,FORENSIC,AND ETHICS CONSULTATION IN MENTAL HEALTH
Gasex
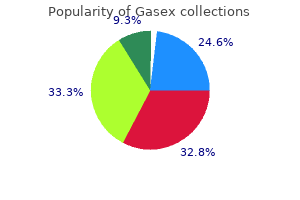
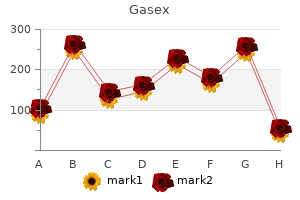
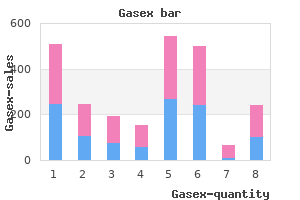
"Purchase gasex online now, gastritis cystica profunda definition".
By: J. Bandaro, MD
Deputy Director, Western Michigan University Homer Stryker M.D. School of Medicine
Abundant osteoblasts and osteoclasts border trabeculae (same case as A and B) (D chronic gastritis rheumatoid arthritis order gasex without a prescription, �100) (D gastritis diet ketogenic order cheap gasex line, hematoxylin-eosin) gastritis fundus cheapest gasex. A gastritis symptoms mayo clinic order gasex 100caps fast delivery, Radiograph with diffuse fusiform cortical thickening and sclerosis of tibial shaft. B, Specimen radiograph of identical case shows resected fragment of anterolateral tibial cortex with dense sclerotic space representing nidus (arrows). C, Anteroposterior radiograph of intramedullary nidus of osteoid osteoma in femoral shaft. Note delicate sclerosis of adjacent cortex and outstanding multilayered periosteal new bone formation. A, Computed tomogram of osteoid osteoma shows wellcircumscribed nidus involving the lateral components of the neural arch. B, Low energy photomicrograph of the nidus tissue shows haphazardly arranged bony trabeculae of woven bone in a background of hypercellular stroma with ample osteoblast and multinucleated osteoclastic large cell (B, �70). C and D, Intermediate power photmicrographs of the nidus tissue exhibiting trabeculae of woven bone rimmed by plump osteoblasts and occasional osteoclastic cells (C and D, �100). A, Anteroposterior plain radiograph with ill-defined sclerosis of the right pedicle of the L1 lumbar vertebra. B, Computed tomogram exhibits well-circumscribed nidus with mineralized center in lamina. C, Whole-mount specimen of the resected posterior neural arch showing a well-circumscribed nidus (arrows). Radiographically and clinically, osteoid osteoma could be confused with inflammatory situations, corresponding to bone abscess and osteomyelitis of acute or persistent sclerosing varieties. This drawback is most evident in osteoid osteomas affecting the small bones of the hands and toes. In juxtaarticular areas, monoarticular rheumatoid arthritis could be simulated microscopically and radiographically because of the associated distinguished lymphoproliferative synovitis. In every of these instances, histologic identification of the nidus tissue disposes of the diagnostic issue. Lesions that current as intracortical lucencies resembling osteoid osteoma include abscesses, hemangiomas and, in very unusual circumstances, intracortical osteosarcomas. In all these entities, constructive findings on bone scans may be anticipated; due to this fact bone scans are of limited diagnostic usefulness in discriminating between osteoid osteoma and the other lesions. In most cases, enostoses, or small bone islands, could be separated from osteoid osteomas by the absence of medical signs, lack of perilesional sclerosis, and usually negative bone isotope scans. This problem could additionally be accentuated by the related distinguished swelling of surrounding gentle tissue. Rarely, accent development facilities may be confused radiologically with osteoid osteoma. The histologic appearance of osteoid osteoma nidus tissue is usually so distinctive that differential diagnostic issues on this level not often happen. B, Low power photomicrograph shows topography of intracortical nidus and surrounding bone. Note sharply demarcated nidus surrounded by sclerotic cortical bone with thickened medullary and periosteal bone trabeculae. C, Resected specimen with a well-demarcated nidus tissue and sclerotic ivory appearance of surrounding bone. D, Radiograph of the specimen shown in C exhibits lucent well-demarcated nidus surrounded by sclerotic bone with thickened trabeculae. E, Radiograph of resected fragment of bone with sharply demarcated oval nidus surrounded by densely sclerotic bone. There is outstanding periosteal response with quite a few parallel spiculae of newly shaped bone. Note sharply demarcated nidus with peripheral lucency and sclerotic trabeculae of surrounding bone.
Syndromes
- Chest x-ray
- Antiviral medications, such as acyclovir (Zovirax) and foscarnet (Foscavir) -- to treat herpes encephalitis or other severe viral infections (however, no specific antiviral drugs are available to fight encephalitis)
- Rash that begins on the chest and spreads to the rest of the body (except the palms of the hands and soles of the feet)
- Excessive bleeding
- Have you eaten shellfish or nuts recently?
- Rusty or brown-colored ring around the iris (Kayser-Fleischer rings)
- Rapid breathing
- Bleeding inside your belly
- Calm and reassure the person. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap. If time allows, and you have some, put on a pair of protective gloves.
- Are over age 30
Primary malignant tumors of bone generally reach substantial dimensions before they produce signs (predominantly ache or pathologic fracture) gastritis rice buy gasex 100 caps mastercard. The likelihood of discovering these related lesions could be facilitated by consideration to clinicopathologic correlation of all available data earlier than arriving at a analysis gastritis antibiotics discount gasex generic. In bone gastritis diet ����������� purchase gasex 100caps without prescription, the inclusion of radiographic imaging knowledge within the diagnostic course of presents a novel alternative to uncover clues to causal relationships that may not be reflected in histologic patterns or in different laboratory information gastritis diet ������ order gasex from india. The relative rarity of malignant transformation in fibrous dysplasia, osteomyelitis, bone cysts, osteogenesis imperfecta, and bone infarction places these situations in a separate category. The potential relationship of secondary malignancy to metallic implants and joint prostheses is a subject of increasing concern, although its statistical validity remains to be in doubt. Additional neoplastic and nonneoplastic lesions that could be precursors of malignancy in bone are listed in Table 24-1. In this chapter the discussion of precancerous lesions is limited to those situations that play a significant role in rising the danger for bone malignancy. From the pathogenetic viewpoint, the disease can be defined by increased transient however progressive and multifocal osteoclastic activity, with bone resorption followed by new bone formation, and finally bone sclerosis. Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical analyses have demonstrated cytoplasmic and nuclear inclusions in the osteoclasts of pagetic bone that are just like those seen in paramyxovirus an infection. This, in flip, elevates ephrinB4 in osteoblastic cells, resulting in the increased bone formation implicated within the growth of pagetoid sclerosis. Autopsy knowledge indicate that it could be found in 3% to 4% of unselected patients older than age forty five years who died of various causes. The fee of familial variants is unclear, and most authors report that less than 10% of circumstances have a familial pattern. A mendelian-dominant sample of transmission has been documented in some families. The full clinical picture with attribute bone deformities seems after 20 to 30 years. Cases with widespread involvement of the skeleton and attribute deformities are rare. The illness in its totally developed scientific picture is typically seen in patients within the sixth through eighth a long time of life. A single bowed and enlarged long bone, such as the tibia or femur, could be the only scientific signal. In most such circumstances, a radiographic examination documents the involvement of further bones. For an outline of the other lesions and their roles as precursors of malignancy in bone, check with the appropriate chapters. The genetic linkage studies have recognized seven predisposing loci that involve 1p12. B, Linear diagram of the p62 protein displaying specific domains and motifs with the place of mutations. When the illness is confined to the epiphyses of lengthy bones, it can be confused on radiographs with different conditions corresponding to giant cell tumor. More consolidated larger areas of sclerosis characterize the ultimate stages of the method. Bowing deformities and pathologic fractures are sometimes seen in weight-bearing websites. Microscopic Findings Microscopically, the initial early part of the illness reveals elevated osteoclastic exercise with fibrosis and distinguished vascularization of the intertrabecular spaces. In addition, prominent osteoblastic activity results in the manufacturing of recent osteoid. The finish of the last phase is dominated by massive areas of bone sclerosis during which multiple irregular lines of mineralization are present. Malignant Transformation the development of bone sarcoma in this condition is essentially the most critical complication and, though unusual, Text continued on p. Note anterior bowing deformity and coarse trabecular sample with obscured corticomedullary demarcation in both radiographs. Lesion is related to pathologic fracture and was thought-about to symbolize big cell tumor. Note large advancing lytic edge at periphery (arrows) and development of bony opacities in central, older areas of lesion (asterisk). D, Specimen radiograph of slice of parietal bone with marked thickening and a quantity of cotton wool opacities that form bigger sclerotic areas.
In addition gastritis diet ����� 100 caps gasex with amex, the background cells may often be polymorphous gastritis hemorrhage purchase gasex 100caps without a prescription, with plasma cells and eosinophils causing frequent confusion with osteomyelitis xanthomatous gastritis order gasex mastercard. To keep away from confusion with reactive or inflammatory problems such as osteomyelitis gastritis symptoms in puppies purchase gasex online from canada, you will want to contemplate the entire clinicopathologic picture. The correct diagnosis is predicated on identification of Reed-Sternberg cells or variants and demonstration of the appropriate immunophenotype by immunohistochemical stains. D, Photomicrograph of lacunar cells with cytoplasmic retraction artifact and lots of background eosinophils (�400). A, Photomicrograph of lacunar cells with cytoplasmic retraction artifact and tons of background eosinophils. Most research require microdissection of Reed-Sternberg cells from the mobile microenvironment. In addition to translocations involving immunoglobulin genes frequent to many B-cell lymphomas, Reed-Sternberg cells have been found to have complicated genetic abnormalities, together with aneuploidy, positive aspects and losses of a number of chromosome loci, and a number of translocations and mutations (Table 12-7). Some of those genetic abnormalities result in deregulation of crucial signaling pathways. ReedSternberg cells have direct and oblique interactions with the surrounding cells and secrete various cytokines and chemokines that appeal to the assorted constituents of the mobile microenvironment. Monocytes flow into in the peripheral blood and could be localized to tissues, especially lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow. Macrophages ingest cells, cellular particles, and microorganisms and secrete inflammatory cytokines. Bone marrow macrophage/dendritic precursors give rise to monocytes and common dendritic precursors. Circulating monocytes give rise to macrophage/ histiocytes and a subset of dendritic cells. Proliferations of monocytic/histiocytic cells range from solitary benign lesions to indolent multifocal disorders to aggressive systemic diseases. Identification of the useful status of monocytic/histiocytic cells and of their interplay with other parts of the immunohematopoietic system provided a basis for contemporary classification of this group of problems. This dialogue is limited to the histiocytic/dendritic cell proliferations that involve the skeleton: Langerhans cell histiocytosis, Erdheim-Chester disease, and Rosai-Dorfman disease (sinus histiocytosis with huge lymphadenopathy). These three ailments have distinctive medical and morphologic findings, however a subset of sufferers could have multiple histiocytosis. Br J Haematol 157:702-708, 2012; Kuppers R: New insights in the biology of Hodgkin lymphoma. Normal Langerhans cells have dendritic processes, and pathologic Langerhans cells have rounded cytoplasmic borders with out classical dendritic cell morphology. Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis occurs in people who smoke and is clinically distinct from different types of Langerhans cell histiocytosis. Langerhans cell sarcoma is a tumor composed of morphologically malignant Langerhans cells. Of the three terms, eosinophilic granuloma continues to be relatively generally used to discuss with unifocal or multifocal bone involvement by Langerhans cell histiocytosis, usually with out involvement of other organ methods. Letterer-Siwe illness was described as an aggressive systemic type of Langerhans cell histiocytosis involving multiple organs and methods with related functional impairment of the affected sites. Frequent sites of involvement in LettererSiwe disease have been lymph nodes, liver spleen, lung, and skin. Approximately 80% of instances are diagnosed in sufferers youthful than age 30 years, and 50% of sufferers are kids youthful than age 10 years. Other frequent websites embody the mandible, vertebral our bodies, ribs, pelvis, and femur. These websites are most frequently involved as solitary lesions however are also sites of predilection in multisystem disease. In the appendicular skeleton, the most important lengthy tubular bones are most incessantly affected. In the long bones, the lesions are predominantly diaphyseal or metaphyseal and virtually by no means lengthen to the end of a bone.
Fewer than 200 instances of articular synovial hemangiomas have been described on the planet literature eosinophilic gastritis diet purchase 100 caps gasex overnight delivery. These lesions virtually solely contain the knee and barely involve the elbow or the ankle gastritis endoscopy purchase gasex australia. Most sufferers have a protracted historical past of dull ache healthy liquid diet gastritis 100 caps gasex sale, limitation of motion 7 day gastritis diet best buy for gasex, and a soft palpable mass. Plain radiographs present an illdefined, periarticular mass, which may comprise phleboliths. An associated degenerative change in the affected joint and cystic lesions in the adjacent bone could additionally be current. The tumor is microscopically identical to an ordinary lipoma in delicate tissue and consists of mature adipose tissue. A, Low energy photomicrograph shows nodular infiltration of histiocytic cells with scattered multinucleated big cells in synovium of tendon sheath. B, High power photomicrograph shows sheets of histiocytes forming coalescent nodules. Cells containing vesicular nuclei with outstanding nucleoli but no cytologic atypia are noted. B and C, Higher magnification of A displaying cords of epithelioid histiocytic cells in hyalinized fibrous stroma. This distinctive function of pigmented villonodular synovitis could be misinterpreted as diagnostic of low-grade epithelioid sclerosing fibrosarcoma. B, Lipoma arborescens representing broad-based polypoid fatty mass attached to synovium of knee joint. Fine, villous fingerlike projections and clubbed fatty polyps are seen studding surface of tumor, which is composed of mature fat. Discrete polypoid lots of adipose tissue, every coated by a delicate synovial lining, are seen with intervening zone of flat, uninvolved synovium. D, Higher magnification of specimen shown in C reveals discrete polypoid masses of yellow adipose tissue. B, Some polypoid buildings represent hyperplastic synovium with chronic irritation. Inset shows fingerlike projection, which represents chronically inflamed synovium. B, Higher magnification of A exhibits adipose tissue within certainly one of polypoid projections. A and B, Prominent vasculature is frequent characteristic of synovial lipomas (A, �50; B, �100) (A and B, hematoxylin-eosin). A, Gross photograph of bivalved synovial nodule from knee of affected person who experienced recurrent hemorrhagic effusions with out trauma. C, Medium power photomicrograph of synovial hemangioma displaying cavernous and capillary vessels. Hopyan S, Nadesan P, Yu C, et al: Dysregulation of hedgehog signalling predisposes to synovial chondromatosis. Ida M, Yoshitake H, Okoch K, et al: An investigation of magnetic resonance imaging features in 14 patients with synovial chondromatosis of the temporomandibular joint. Nakanishi S, Sskamoto K, Yoshitake H, et al: Bone morphogenetic proteins are involved within the pathobiology of synovial chondromatosis. Shearer H, Stern P, Brubacher A, et al: A case report of bilateral synovial chondromatosis of the ankle. Trias A, Quintana O: Synovial chondrometaplasia: evaluate of world literature and examine of 18 Canadian cases. Geldyyev A, Koleganova N, Piecha G, et al: High expression stage of bone degrading proteins as a attainable inducer of osteolytic options in pigmented villonodular synovitis. Gonzalez-Campora R, Salas Herrero E, Otal-Salaverri C, et al: Diffuse tenosynovial large cell tumor of soft tissues: report of a case with cytologic and cytogenetic findings. Mertens F, Orndal C, Mandahl N, et al: Chromosome aberrations in tenosynovial giant cell tumors and nontumorous synovial tissue. Nakashima M, Uchida T, Tsukazaki T, et al: Expression of tyrosine kinase receptors Tie-1 and Tie-2 in big cell tumor of the tendon sheath: a potential role in synovial proliferation.
Buy gasex 100 caps with amex. Juicing Q&A: The best time to drink juice.